ITIL 4 has rolled out a new model for value creation: the Service Value System. This system is representative of how all the components and activities of an organization come together to facilitate value creation through IT-enabled services. Central to this system is the Service Value Chain. This is an operating model for delivery of services through six key activities, which can be combined in a variety of ways to provide a flexible set of value streams.
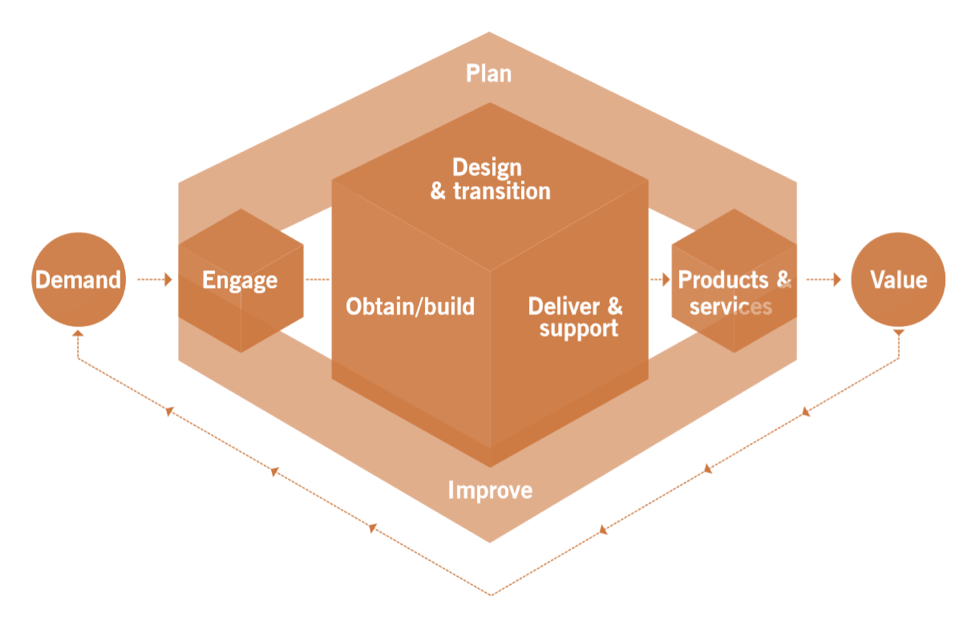
Because of its flexibility the Service Value Chain can support numerous approaches to service delivery, including DevOps and centralized IT. This also allows for new or emerging methodologies, making the Service Value Chain highly adaptable and resilient to changing requirements.
Value Streams
While the activities in the value chain are universal, and high-level key inputs and outputs are a solid foundation, individual value streams are created for specific purposes. As an example, consider the value stream for resolving an E-mail Incident. If we consider all the resources, practices, activities, inputs and outputs, the value stream might look something like this:
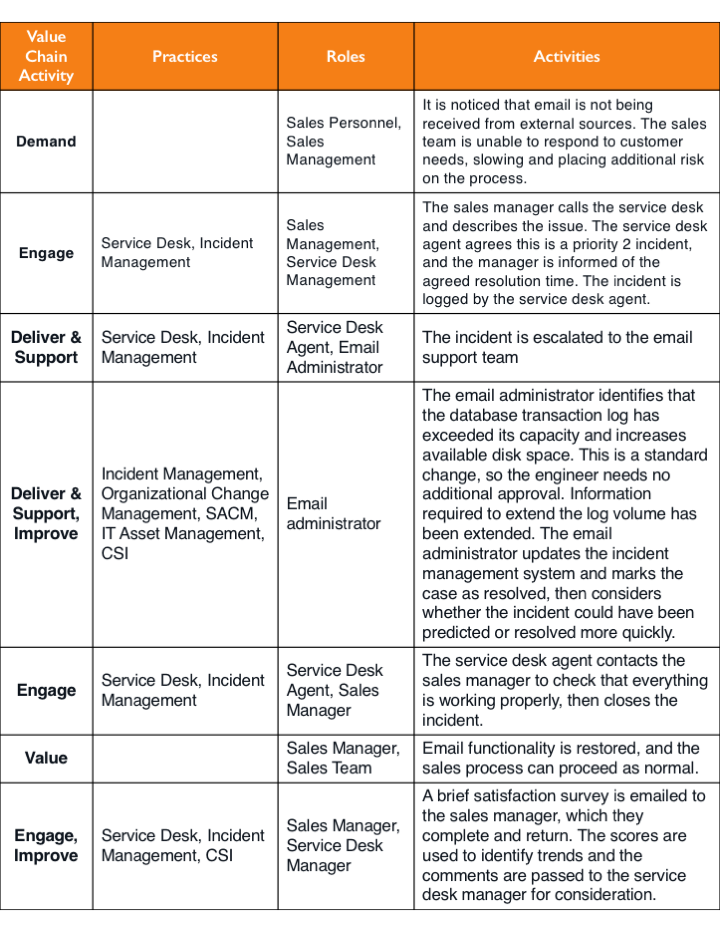
Key Service Value Chain Activities
The six key activities of the Service Value Chain are Plan, Improve, Engage, Design and Transition, Obtain/Build, and Deliver and Support. Each of these contributes to value creation by transforming various inputs into specific outputs. These inputs may be external, or they may come from other activities within the value chain itself. Each activity is supported by one or more Practices. This combination of Service Value Chain activities and practices is then transformed into a value stream for specific tasks, or to respond to situations.
The Service Value Chain has key inputs and outputs for each activity. Inputs can come from external sources, such as Governance; they also come from other activities in the Service Value Chain, such as Improve, Engage, and Obtain/Build. Similarly, outputs can be provided to external consumers, as well as to other activities within the Service Value Chain.
Plan
The Plan activity ensures understanding of the vision, current status, and improvement direction for all four dimensions, as well as products and services across the organization. This is a very strategic activity.
Improve
The Improve activity’s purpose is the continual improvement of products, services and practices across all the Service Value Chain activities and the four dimensions of service management.
Engage
The Engage activity provides understanding of stakeholder needs, transparency, and good relationships with all stakeholders. This activity takes requirements from customers and transforms them into design requirements for the Design and Transition activity.
Design and Transition
Design and Transition ensures that services and products meet stakeholder expectations, considering quality, cost and time-to-market. The primary focus is to take the requirements from Engage and provide specifications for Obtain/Build. This activity also delivers new and changed services and products to the Deliver and Support activity.
Obtain/Build
The Obtain/Build activity is responsible for ensuring that all service components are available when and where needed, and that they meet the agreed specifications. Requirements delivered by Design and Transition are transformed into service components that are, in turn, provided to the Deliver and Support activity, as well as to Design and Transition.
Deliver and Support
Deliver and Support delivers services and products to the customer, ensuring that such delivery meets agreed specifications and the stakeholders’ expectations. This is where the proverbial rubber meets the road, and where the customer sees and co-creates value. Its primary inputs are the services and products delivered by Design and Transition, as well as service components delivered by Obtain/Build.
As one can see, each activity engages in a highly interdependent lifecycle, all leading to value creation for stakeholders. Individual streams include specific roles and responsibilities, and these are dependent on the service or product being provided. As each activity transforms its inputs to specific outputs, new activities take over, further developing the overall value chain. The Improve activity is the overarching guide to gradual and continual improvement in all activities and value streams.
The Service Value Chain exists as the core of the ITIL 4 Service Value System, it is informed and impacted by each of the other aspects of the Service Value System. Through this interaction and the six key activities of the Service Value Chain, value is delivered to stakeholders in the form of services and products.



